MirrorPad
tensorflow C++ API
Pads a tensor with mirrored values.
Summary
This operation pads ainputwith mirrored values according to thepaddingsyou specify.paddingsis an integer tensor with shape[n, 2], where n is the rank ofinput. For each dimension D ofinput,paddings[D, 0]indicates how many values to add before the contents ofinputin that dimension, andpaddings[D, 1]indicates how many values to add after the contents ofinputin that dimension. Bothpaddings[D, 0]andpaddings[D, 1]must be no greater thaninput.dim_size(D)(orinput.dim_size(D) - 1) ifcopy_borderis true (if false, respectively).
The padded size of each dimension D of the output is:
paddings(D, 0) + input.dim_size(D) + paddings(D, 1)
For example:
``` 't' is [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]].
'paddings' is [[1, 1]], [2, 2]].
'mode' is SYMMETRIC.
rank of 't' is 2.
pad(t, paddings) ==> [[2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2] [2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2] [5, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 5] [5, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 5]] ```
Arguments:
- scope: A Scope object
- input: The input tensor to be padded.
- paddings: A two-column matrix specifying the padding sizes. The number of rows must be the same as the rank of
input. - mode: Either
REFLECTorSYMMETRIC. In reflect mode the padded regions do not include the borders, while in symmetric mode the padded regions do include the borders. For example, ifinputis[1, 2, 3]andpaddingsis[0, 2], then the output is[1, 2, 3, 2, 1]in reflect mode, and it is[1, 2, 3, 3, 2]in symmetric mode.
Returns:
Output: The padded tensor.
MirrorPad block
Source link :https://github.com/EXPNUNI/enuSpaceTensorflow/blob/master/enuSpaceTensorflow/tf_array_ops.cpp
Argument:
- Scope scope : A Scope object (A scope is generated automatically each page. A scope is not connected.)
- Input
input: A N-DTensor. - Input
paddings: ATensortype ofint32,int64(Must be one integer type). A two-column matrix specifying the padding sizes. The number of rows must be the same as the rank ofinput. ex) input shape -> [3][3][3], paddings shape -> [3][2] - StringPiece
mode: EitherREFLECTorSYMMETRIC. In reflect mode the padded regions do not include the borders, while in symmetric mode the padded regions do include the borders. For example, ifinputis[1, 2, 3]andpaddingsis[0, 2], then the output is[1, 2, 3, 2, 1]in reflect mode, and it is[1, 2, 3, 3, 2]in symmetric mode.
Output:
- Output output : Output object of MirrorPad class object.
Result:
- std::vector(Tensor)
result_output: ATensor.paddings(D, 0) + input.dim_size(D) + paddings(D, 1)
Using Method
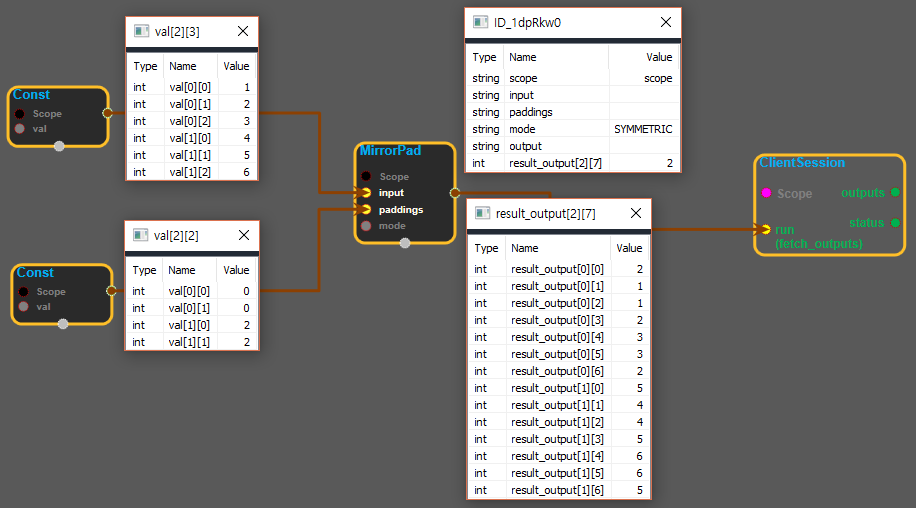 ※input의 shape가 [2][3], 값이 [[1,2,3][4,5,6]]이고, paddings가 [2][2]에 [[0,0][2,2]], mode가 "SYMMETRIC"일 때 결과는 [[2,1,1,2,3,3,2][5,4,4,5,6,6,5]]이다. mode가 "REFLECT"일 때 결과는 [[3,2,1,2,3,2,1][6,5,4,5,6,5,4]] 이다.
※input의 shape가 [2][3], 값이 [[1,2,3][4,5,6]]이고, paddings가 [2][2]에 [[0,0][2,2]], mode가 "SYMMETRIC"일 때 결과는 [[2,1,1,2,3,3,2][5,4,4,5,6,6,5]]이다. mode가 "REFLECT"일 때 결과는 [[3,2,1,2,3,2,1][6,5,4,5,6,5,4]] 이다.
※paddings에 들어가는 값은 [D][0]은 input에 들어있는 값의 앞에 들어가는 padding값 이고(input이 [1,2,3]이고, padding이 [2,0], mode 가 SYMMETRIC일 때 값은 [2,1,1,2,3]이다. mode가 REFLECT라면 [3,2,1,2,3]이다.), [D][1]은 input에 들어있는 값의 뒤에 들어가는 padding값이다(input이 [1,2,3]이고, padding이 [0,2], mode 가 SYMMETRIC일 때 값은 [1,2,3,3,2]이다. mode가 REFLECT라면 [1,2,3,2,1]이다.).