SpaceToBatch
tensorflow C++ API
SpaceToBatch for 4-D tensors of type T.
Summary
This is a legacy version of the more generalSpaceToBatchND.
Zero-pads and then rearranges (permutes) blocks of spatial data into batch. More specifically, this op outputs a copy of the input tensor where values from theheightandwidthdimensions are moved to thebatchdimension. After the zero-padding, bothheightandwidthof the input must be divisible by the block size.
Arguments:
- scope: A Scope object
- input: 4-D with shape
[batch, height, width, depth]. paddings: 2-D tensor of non-negative integers with shape
[2, 2]. It specifies the padding of the input with zeros across the spatial dimensions as follows:paddings =[[pad_top, pad_bottom],[pad_left, pad_right]]The effective spatial dimensions of the zero-padded input tensor will be:
height_pad = pad_top + height + pad_bottom width_pad = pad_left + width + pad_right
The attrblock_sizemust be greater than one. It indicates the block size.
- Non-overlapping blocks of size
block_size x block sizein the height and width dimensions are rearranged into the batch dimension at each location. - The batch of the output tensor is
batch * block_size * block_size. - Both height_pad and width_pad must be divisible by block_size.
The shape of the output will be:
[batch*block_size*block_size, height_pad/block_size, width_pad/block_size, depth]
Some examples:
(1) For the following input of shape[1, 2, 2, 1]and block_size of 2:
``` x = [[[[1], [2]], [[3], [4]]]] ```
The output tensor has shape[4, 1, 1, 1]and value:
``` [[[[1]]], [[[2]]], [[[3]]], [[[4]]]] ```
(2) For the following input of shape[1, 2, 2, 3]and block_size of 2:
``` x = [[[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]]] ```
The output tensor has shape[4, 1, 1, 3]and value:
``` [[[1, 2, 3]], [[4, 5, 6]], [[7, 8, 9]], [[10, 11, 12]]] ```
(3) For the following input of shape[1, 4, 4, 1]and block_size of 2:
``` x = [[[[1], [2], [3], [4]], [[5], [6], [7], [8]], [[9], [10], [11], [12]], [[13], [14], [15], [16]]]] ```
The output tensor has shape[4, 2, 2, 1]and value:
``` x = [[[[1], [3]], [[9], [11]]], [[[2], [4]], [[10], [12]]], [[[5], [7]], [[13], [15]]], [[[6], [8]], [[14], [16]]]] ```
(4) For the following input of shape[2, 2, 4, 1]and block_size of 2:
``` x = [[[[1], [2], [3], [4]], [[5], [6], [7], [8]]], [[[9], [10], [11], [12]], [[13], [14], [15], [16]]]] ```
The output tensor has shape[8, 1, 2, 1]and value:
``` x = [[[[1], [3]]], [[[9], [11]]], [[[2], [4]]], [[[10], [12]]], [[[5], [7]]], [[[13], [15]]], [[[6], [8]]], [[[14], [16]]]] ```
Among others, this operation is useful for reducing atrous convolution into regular convolution.
Returns:
Output: The output tensor.
SpaceToBatch block
Source link :https://github.com/EXPNUNI/enuSpaceTensorflow/blob/master/enuSpaceTensorflow/tf_array_ops.cpp
Argument:
- Scope scope : A Scope object (A scope is generated automatically each page. A scope is not connected.)
- Input
input: 4-D with shape [batch, height, width, depth]. - Input
paddings: 2-D tensor of non-negative integers with shape[2, 2] - Int64
block_size: must be greater than one. It indicates the block size.
Output:
- Output output: Output object of SpaceToBatch class object.
Result:
- std::vector(Tensor)
result_output: The output tensor.
Using Method
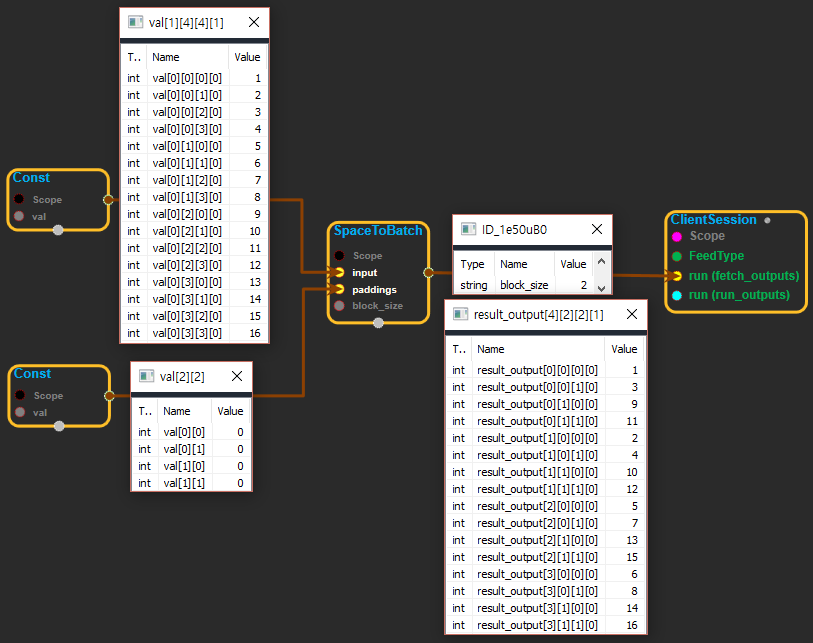
※ BatchToSpace와 반대되는 기능을 한다. input을 재정렬하며 input의 마지막 차원은 shape의 크기가 변하지 않는다.