ScatterNd
tensorflow C++ API
Scatter updates into a new (initially zero) tensor according to indices .
Summary
Creates a new tensor by applying sparseupdatesto individual values or slices within a zero tensor of the givenshapeaccording to indices. This operator is the inverse of the tf.gather_nd operator which extracts values or slices from a given tensor.
WARNING: The order in which updates are applied is nondeterministic, so the output will be nondeterministic ifindicescontains duplicates.
indicesis an integer tensor containing indices into a new tensor of shapeshape. The last dimension ofindicescan be at most the rank ofshape:
indices.shape[-1]<= shape.rank
The last dimension ofindicescorresponds to indices into elements (ifindices.shape[-1] = shape.rank) or slices (ifindices.shape[-1] < shape.rank) along dimensionindices.shape[-1]ofshape.updatesis a tensor with shape
indices.shape[:-1]+ shape[indices.shape[-1]:]
The simplest form of scatter is to insert individual elements in a tensor by index. For example, say we want to insert 4 scattered elements in a rank-1 tensor with 8 elements.
In Python, this scatter operation would look like this:
```python indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1], [7]]) updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12]) shape = tf.constant([8]) scatter = tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape) with tf.Session() as sess: print(sess.run(scatter)) ```
The resulting tensor would look like this:
[0,11,0,10,9,0,0,12]
We can also, insert entire slices of a higher rank tensor all at once. For example, if we wanted to insert two slices in the first dimension of a rank-3 tensor with two matrices of new values.
In Python, this scatter operation would look like this:
```python indices = tf.constant([[0], [2]]) updates = tf.constant([[[5, 5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6, 6], [7, 7, 7, 7], [8, 8, 8, 8]], [[5, 5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6, 6], [7, 7, 7, 7], [8, 8, 8, 8]]]) shape = tf.constant([4, 4, 4]) scatter = tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape) with tf.Session() as sess: print(sess.run(scatter)) ```
The resulting tensor would look like this:
[[[5,5,5,5],[6,6,6,6],[7,7,7,7],[8,8,8,8]],
[[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0]],
[[5,5,5,5],[6,6,6,6],[7,7,7,7],[8,8,8,8]],
[[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0]]]
Arguments:
- scope: A Scope object
- indices: Index tensor.
- updates: Updates to scatter into output.
- shape: 1-D. The shape of the resulting tensor.
Returns:
Output: A new tensor with the given shape and updates applied according to the indices.
ScatterNd block
Source link :https://github.com/EXPNUNI/enuSpaceTensorflow/blob/master/enuSpaceTensorflow/tf_array_ops.cpp
Argument:
- Scope scope : A Scope object (A scope is generated automatically each page. A scope is not connected.)
- Input
indices: Index tensor. - Input
updates: Updates to scatter into output. - Input
shape: 1-D. The shape of the resulting tensor.
Output:
- Output
output: Output object of ScatterNd class object.
Result:
- std::vector(Tensor)
result_output: A new tensor with the given shape and updates applied according to the indices.
Using Method
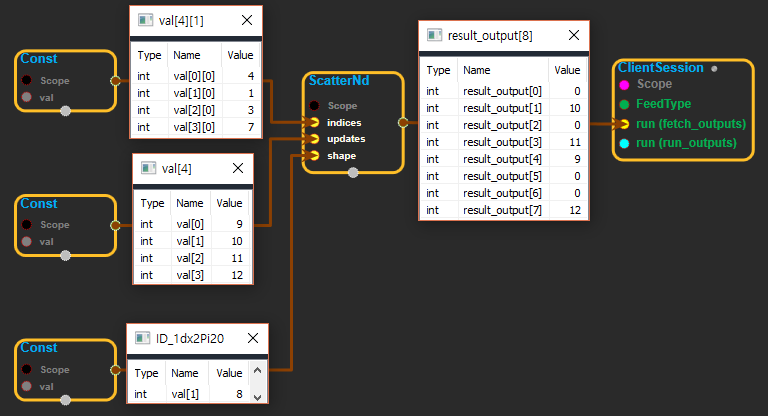
※ update의 데이터를 indices에 있는 인덱스 순서대로 shape입력 값의 모양으로 된 텐서에 입력한다. 이때 빈칸은 0으로 채운다.
※ shape 입력 값은 indices의 shape에서 -1 rank한 값과 update의 shape값을 랭크 별로 더한 값이다. (ex: indice의 shape는 [2,1]이고, update의 shape가 [2,4,4]라면 -> [2] + [2,4,4] = [4,4,4] )