StridedSliceAssign
tensorflow C++ API
tensorflow::ops::StridedSliceAssign
Assign value to the sliced l-value reference of ref.
Summary
The values ofvalueare assigned to the positions in the variablerefthat are selected by the slice parameters. The slice parametersbegin,end,strides, etc. work exactly as inStridedSlice`.
NOTE this op currently does not support broadcasting and sovalue's shape must be exactly the shape produced by the slice ofref.
Arguments:
- scope: A Scope object
Returns:
Output: The output_ref tensor.
StridedSliceAssign block
Source link :https://github.com/EXPNUNI/enuSpaceTensorflow/blob/master/enuSpaceTensorflow/tf_array_ops.cpp
Argument:
- Scope scope : A Scope object (A scope is generated automatically each page. A scope is not connected.)
- Input ref: A
Tensor. - Input begin: An
int32orint64 Tensor. `begin[k]` specifies the offset into the `k`th range specification. The exact dimension this corresponds to will be determined by context. Out-of-bounds values will be silently clamped. If the `k`th bit of `begin_mask` then `begin[k]` is ignored and the full range of the appropriate dimension is used instead. Negative values causes indexing to start from the highest element e.g. If `foo==[1,2,3]` then `foo[-1]==3`. - Input end: An
int32orint64 Tensor. `end[i]` is like `begin` with the exception that `end_mask` is used to determine full ranges. - Input strides: An
int32orint64 Tensor. `strides[i]` specifies the increment in the `i`th specification after extracting a given element. Negative indices will reverse the original order. Out or range values are clamped to `[0,dim[i]) if slice[i]>0or[-1,dim[i]-1] if slice[i] < 0` - Input value: A
Tensor. Assign to ref. - StridedSlice::Attrs attrs:
- begin_mask: a bitmask where a bit i being 1 means to ignore the begin value and instead use the largest interval possible. At runtime begin[i] will be replaced with
[0, n-1) ifstride[i] > 0or[-1, n-1]ifstride[i] < 0 - end_mask: analogous to begin_mask
- shrink_axis_mask: a bitmask where bit i implies that the i th specification should shrink the dimensionality. begin and end must imply a slice of size 1 in the dimension. For example in python one might do foo[:, 3, :] which would result in shrink_axis_mask being 2.
- ellipsis_mask: a bitmask where bit i being 1 means the i`th position is actually an ellipsis. One bit at most can be 1. If ellipsis_mask == 0, then an implicit ellipsis mask of 1 << (m+1) is provided. This means that foo[3:5] == foo[3:5, ...]. An ellipsis implicitly creates as many range specifications as necessary to fully specify the sliced range for every dimension. For example for a 4-dimensional tensor foo the slice foo[2, ..., 5:8] implies foo[2, :, :, 5:8].
- new_axis_mask: a bitmask where bit i being 1 means the i th specification creates a new shape 1 dimension. For example foo[:4, tf.newaxis, :2] would produce a shape (4, 1, 2) tensor.
- begin_mask: a bitmask where a bit i being 1 means to ignore the begin value and instead use the largest interval possible. At runtime begin[i] will be replaced with
Output:
- Output output: Output object of StridedSliceAssign class object.
Result:
- std::vector(Tensor)
result_output: ATensorthe same type asinput.
Using Method
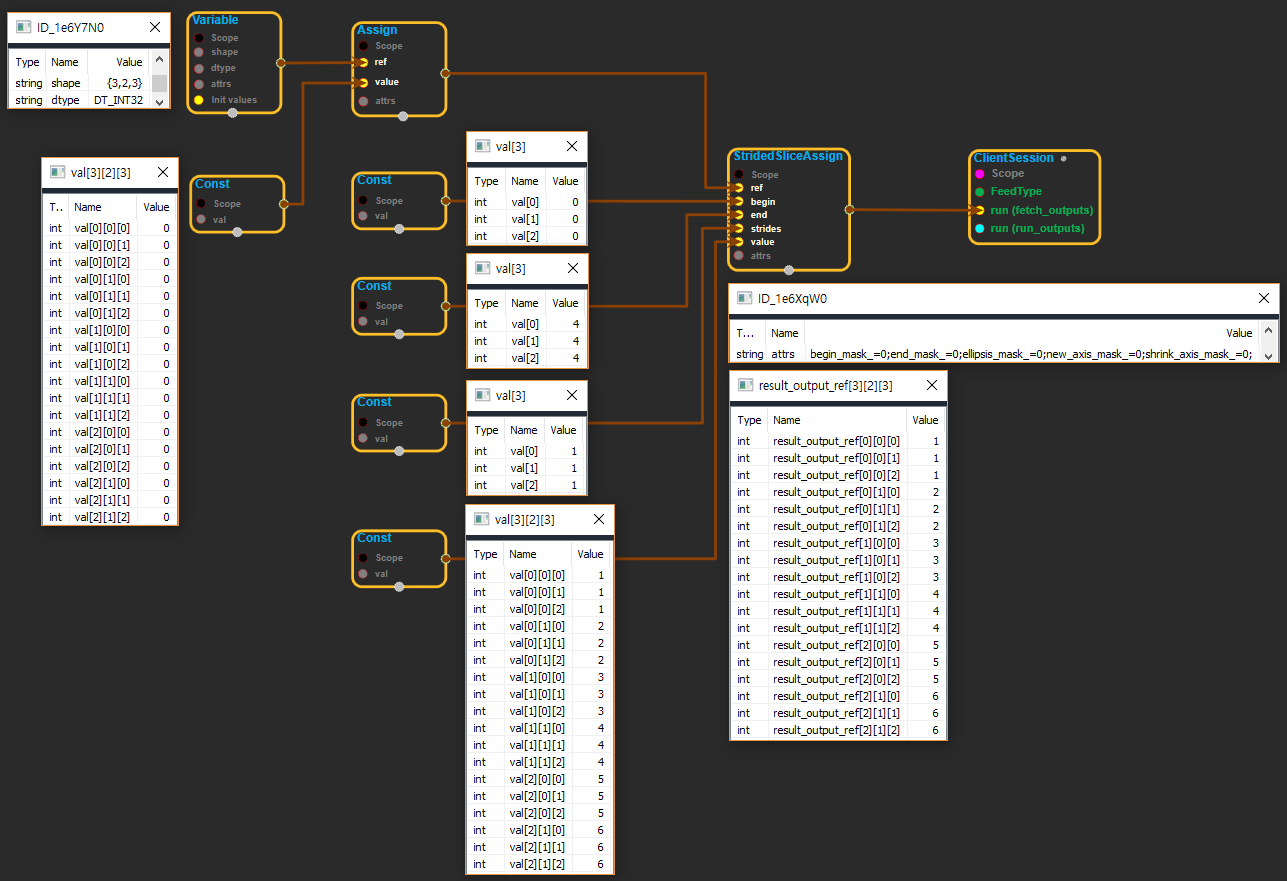 ※ value에서 특정한 부분을 잘라내어 ref의 variable에 입력하는 기능을 한다. begin은 각 차원에서 잘라낼 시작지점(마이너스 값일 경우 reverse시키는것으로 보임), end는 어디까지 자를것인지 입력한다. strides는 몇 스텝을 이동할 것인지 정한다(ex: strides가 2일 경우 시작인 1에서 두칸 넘어간 3 그다음은 5 이런식이다.).
※ value에서 특정한 부분을 잘라내어 ref의 variable에 입력하는 기능을 한다. begin은 각 차원에서 잘라낼 시작지점(마이너스 값일 경우 reverse시키는것으로 보임), end는 어디까지 자를것인지 입력한다. strides는 몇 스텝을 이동할 것인지 정한다(ex: strides가 2일 경우 시작인 1에서 두칸 넘어간 3 그다음은 5 이런식이다.).